Subflow Loop
Building upon the capabilities of Subflow Node, we are excited to introduce the Subflow Loop Node. This powerful addition enhances your flow logic by enabling iteration over multiple data sets within a subflow, supporting the creation of more complex and dynamic workflows.
Understanding the Loop Mechanism
The Subflow Loop Node efficiently handles repetitive tasks by iterating over specified fields within a subflow. This mechanism allows your flows to seamlessly process lists of data, executing subflow logic for each item in the list. Below is a detailed explanation of how the loop mechanism operates:
Overview
Loop Fields: These are input fields designated for iteration. Each loop field must receive a list, enabling the Subflow Loop Node to process each element individually.
Maximum Iterations: To prevent excessive processing, the Subflow Loop Node enforces a maximum number of iterations. If the number of items in the loop fields exceeds this limit, an error is triggered.
How It Works
Input Validation: The node verifies the presence of necessary subflow data and ensures that all loop fields contain lists. It also checks that all loop fields have the same length to maintain consistency across iterations.
Determining Iterations: The number of iterations is determined by the length of the longest loop field. All loop fields must have matching lengths to avoid mismatches.
Executing the Subflow: The node executes the subflow logic for each iteration, using the prepared parameters.
Aggregating Outputs: Outputs from each iteration are collected and combined to produce the final result.
Streaming and Final Output: Intermediate results are streamed for real-time visualization, and the final aggregated output is returned once all iterations are complete.
Tutorial
To illustrate the Subflow Loop Node, we will use a basic example flow. In this flow, the node generates a line of text for each subject using GPT.
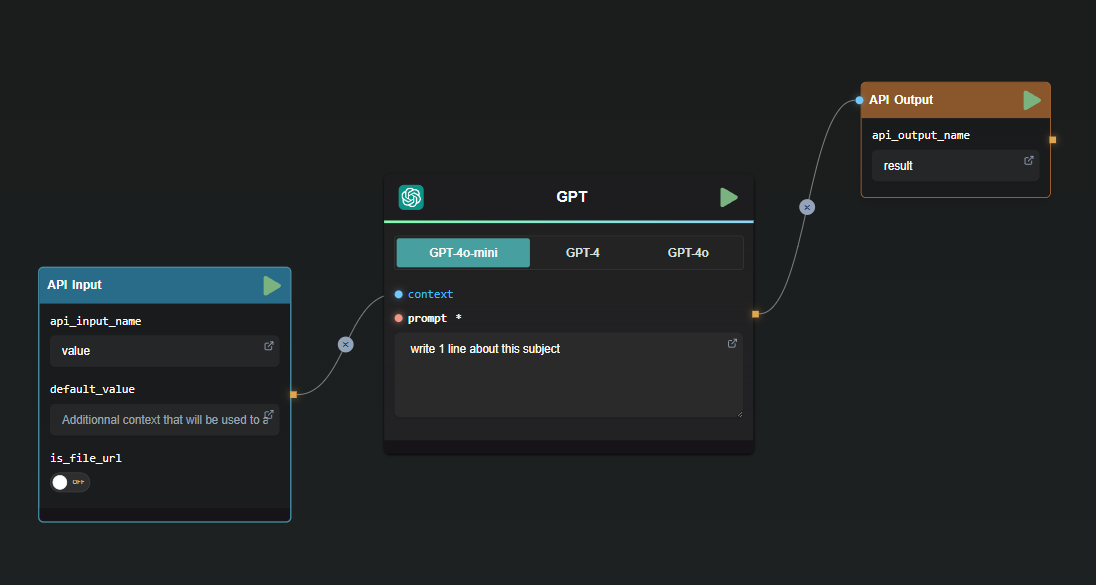
Setting Up the Subflow Loop Node
Drag and Drop the Subflow Loop Node
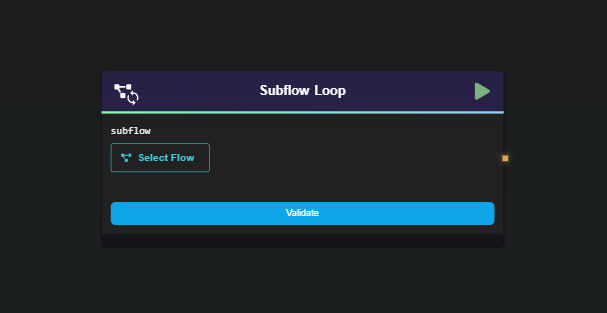
Select the Subflow: Choose the subflow containing the logic you want to iterate over, then validate your selection.
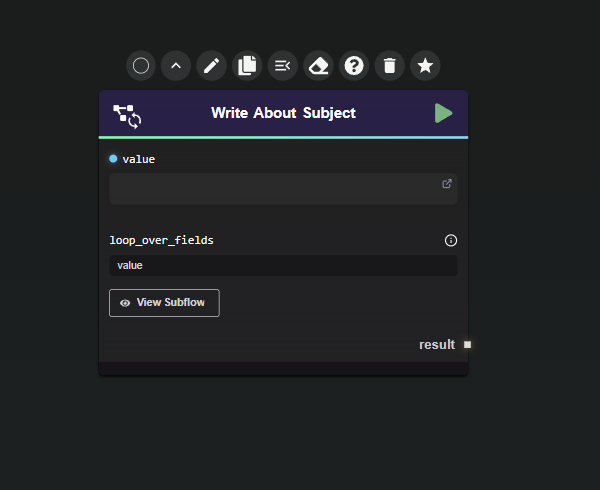
Define Loop Fields: Select the input fields to be looped over in the loop_over_fields list. Ensure that each designated field receives a list as input.
- For this example, the field is named
value. It will be the looped field, while others remain constant during iterations.
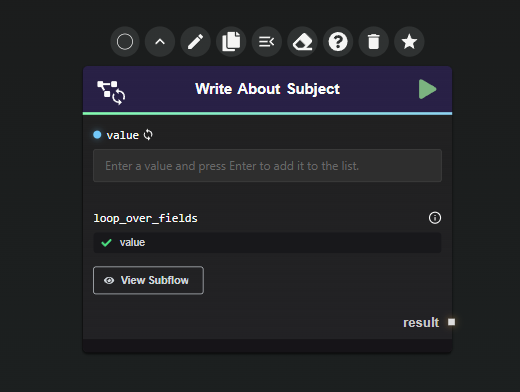
- For this example, the field is named
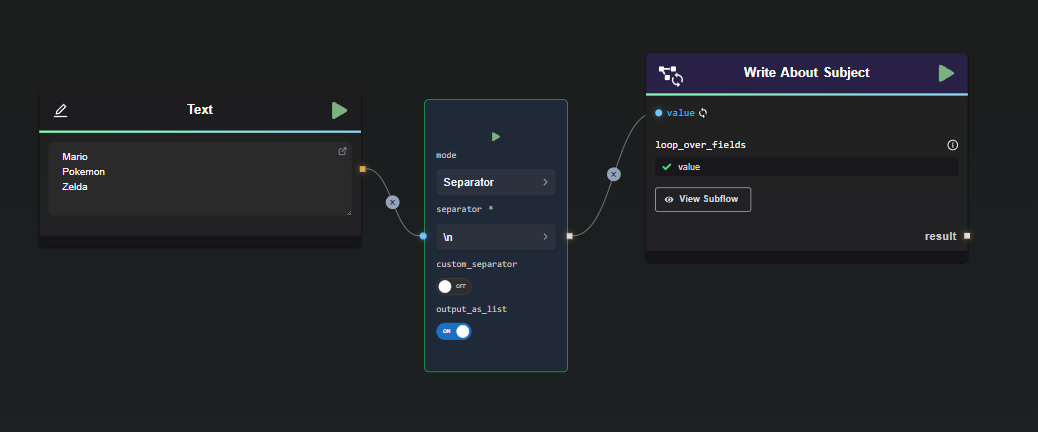
Connect a List Input: Connect a list input to the selected fields. You can achieve this using a Data Splitter with the
output_as_listoption enabled, or by entering the list directly into the input field.Example with List Node:
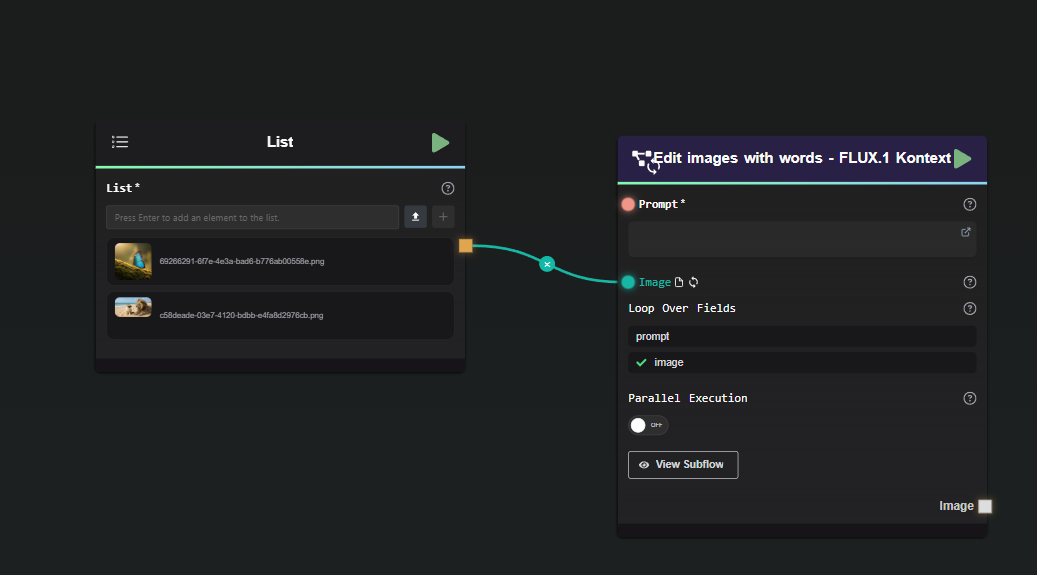
Example with Data Splitter:
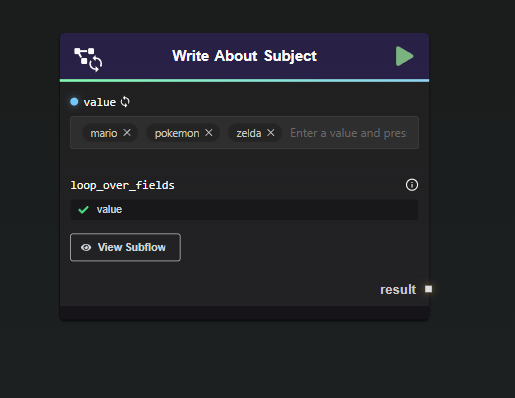
Direct input method:
Other nodes that can serve as loop inputs:
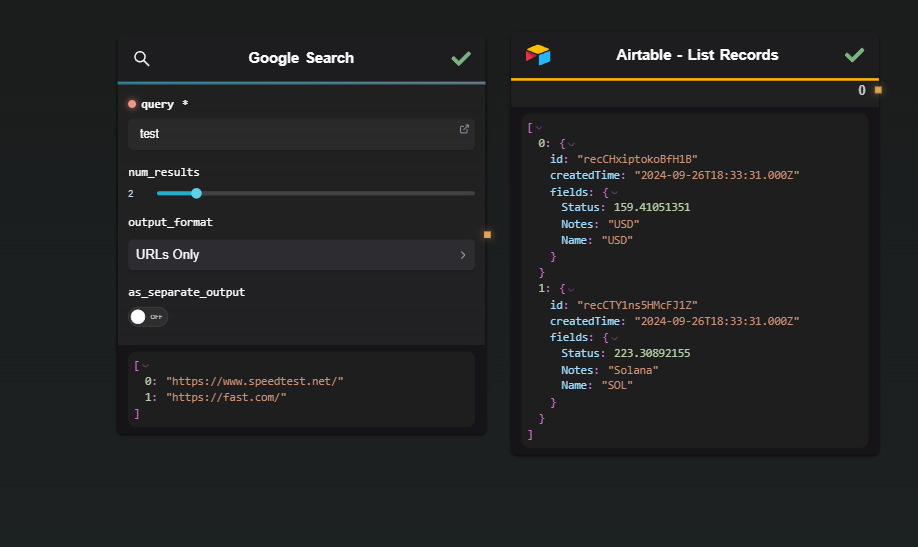
Run the Node
The Subflow Loop Node outputs a list of results. If the subflow has multiple defined outputs, the result will be a list for each output.
In this example, the subflow has a single output, resulting in one list with three elements:
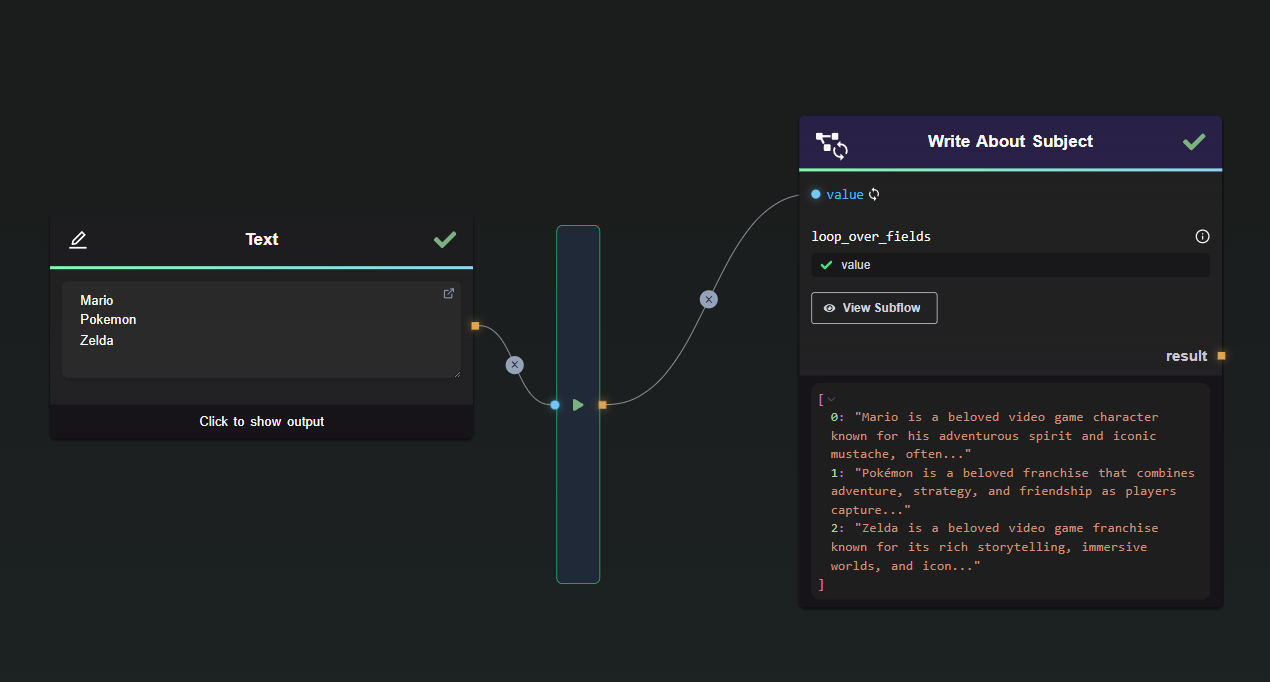
The output can then be used as input for additional processing, including nesting in another Subflow Loop Node.
Comparing Approaches
By combining the Subflow Loop Node with tools like the Data Splitter or Regex Extractor, you can dynamically generate content without being limited to a fixed number of outputs. Previously, workflows required a predefined number of outputs and individual processing nodes.
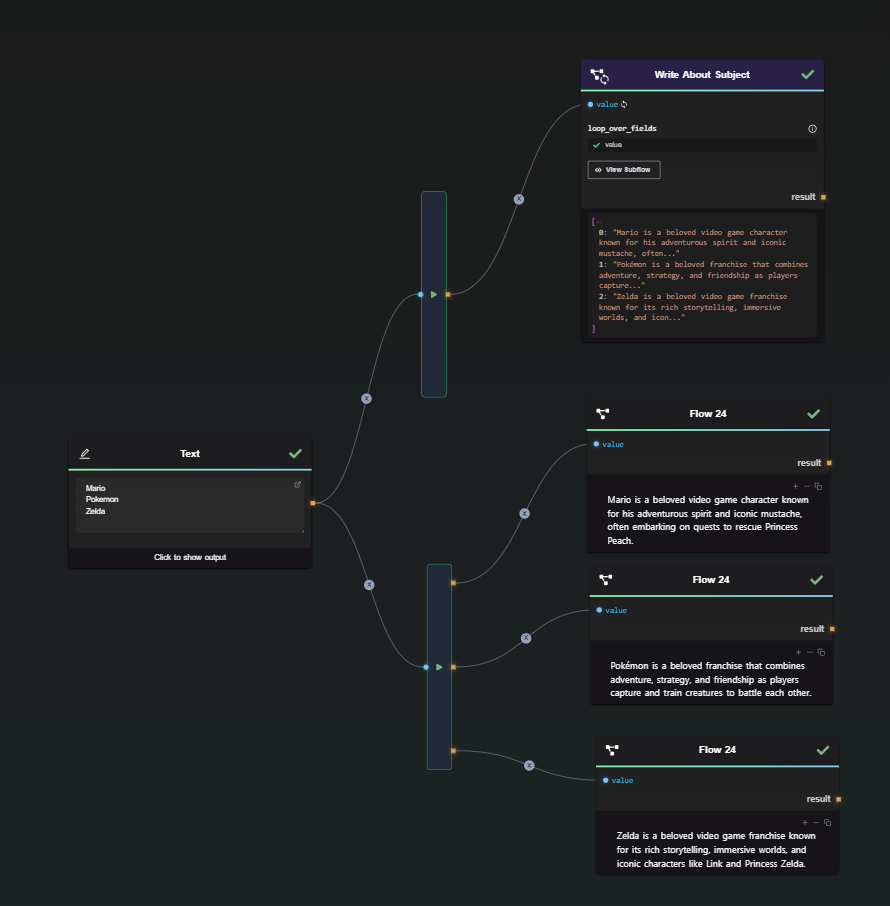
Best Practices
- Consistent List Lengths: Ensure all loop fields have lists of the same length to avoid runtime errors.
- Monitor Nested Loops: While nested Subflow Loops are supported, excessive nesting can complicate debugging and maintenance. Aim for a balance between complexity and clarity.
Conclusion
The Subflow Loop Node significantly enhances the flexibility and efficiency of your flow-based applications by enabling seamless iteration over data sets within subflows. By abstracting repetitive tasks into a reusable node, you can simplify workflows, improve maintainability, and maximize the power of your application.
For more detailed guidance and advanced configurations, refer to our Additional Resources section below.