Airtable Node
The Airtable Node provides seamless integration between your workflows and Airtable, enabling you to interact directly with your Airtable bases and tables through a straightforward interface. This node supports several essential operations to manage and automate your Airtable data.
The node now exposes five single-record actions—they cover 90% of typical use cases. Many templates are available in the AI-Flow App to showcase how to use these nodes in real-world scenarios (e.g., update records through a loop, generate an image and save it as an attachment, create a record with AI-generated content). Please refer to these templates first to understand how to take full advantage of the nodes, as this documentation provides a node-by-node reference.
Bulk variants (…Records) still exist for power users; they accept raw JSON arrays but function identically under the hood.
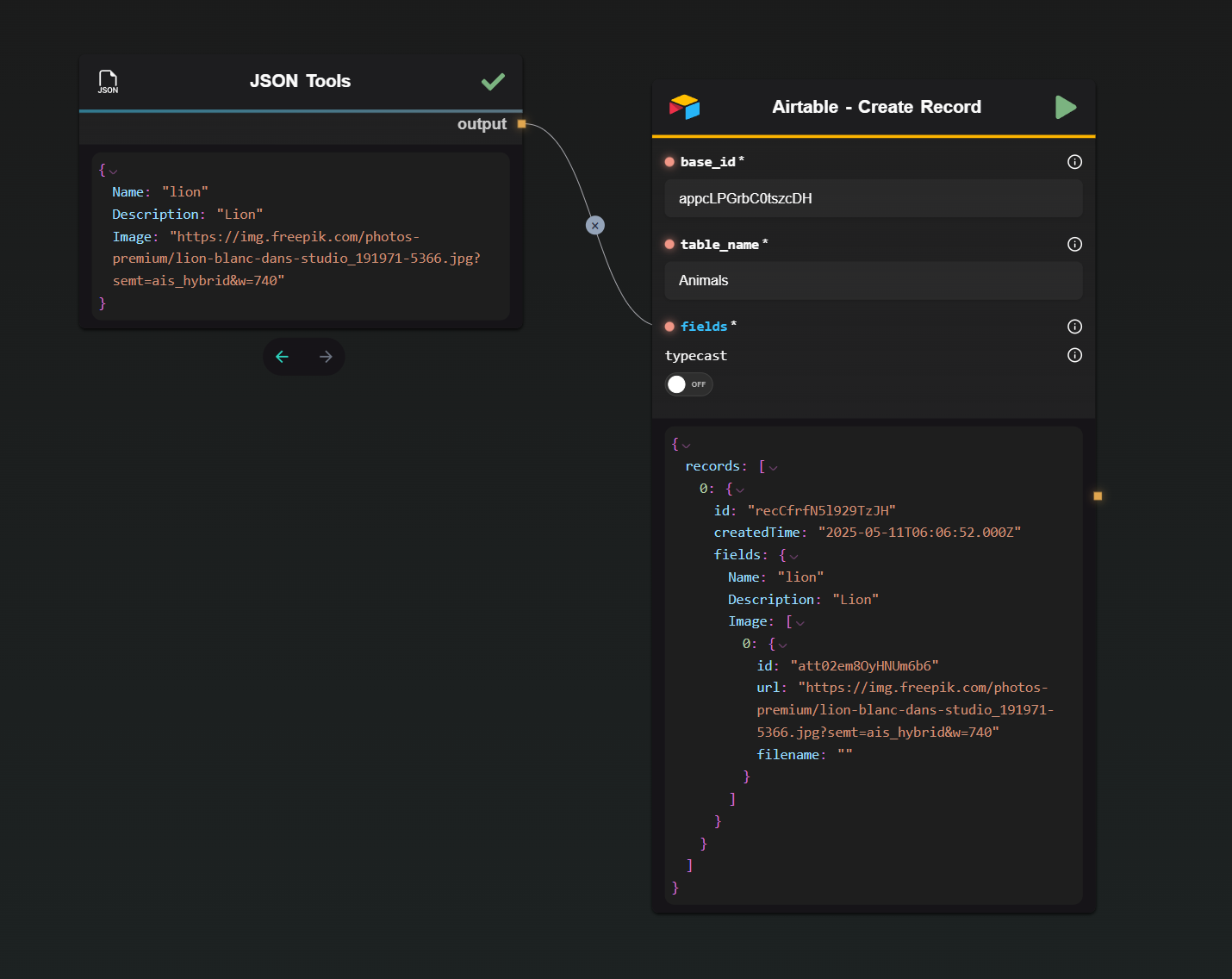
1 · Create Record
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID | The Airtable base you’re using. |
| Table Name | The table that will receive the new record. |
| Fields (JSON) | The record data. Only include the fields you want to set. |
| Typecast | Allows Airtable to coerce strings into collaborators, selects, etc. |
Returns the created record as JSON.
2 · Get Record
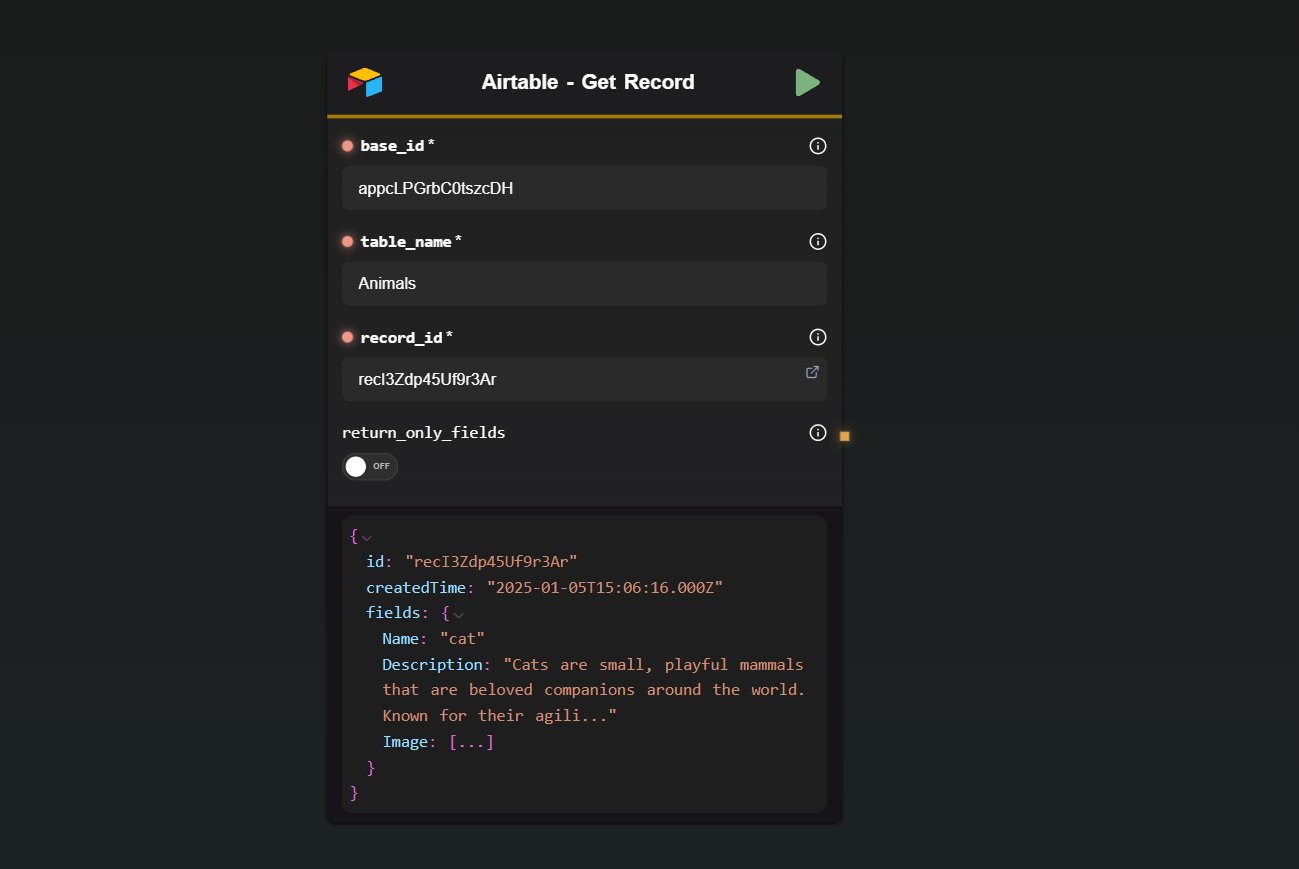
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID | The base to query. |
| Table Name | The table to query. |
| Record ID | The Airtable record ID (recXXXXXXXXX). |
| Fields Only | If on, returns just the fields instead of the full response. |
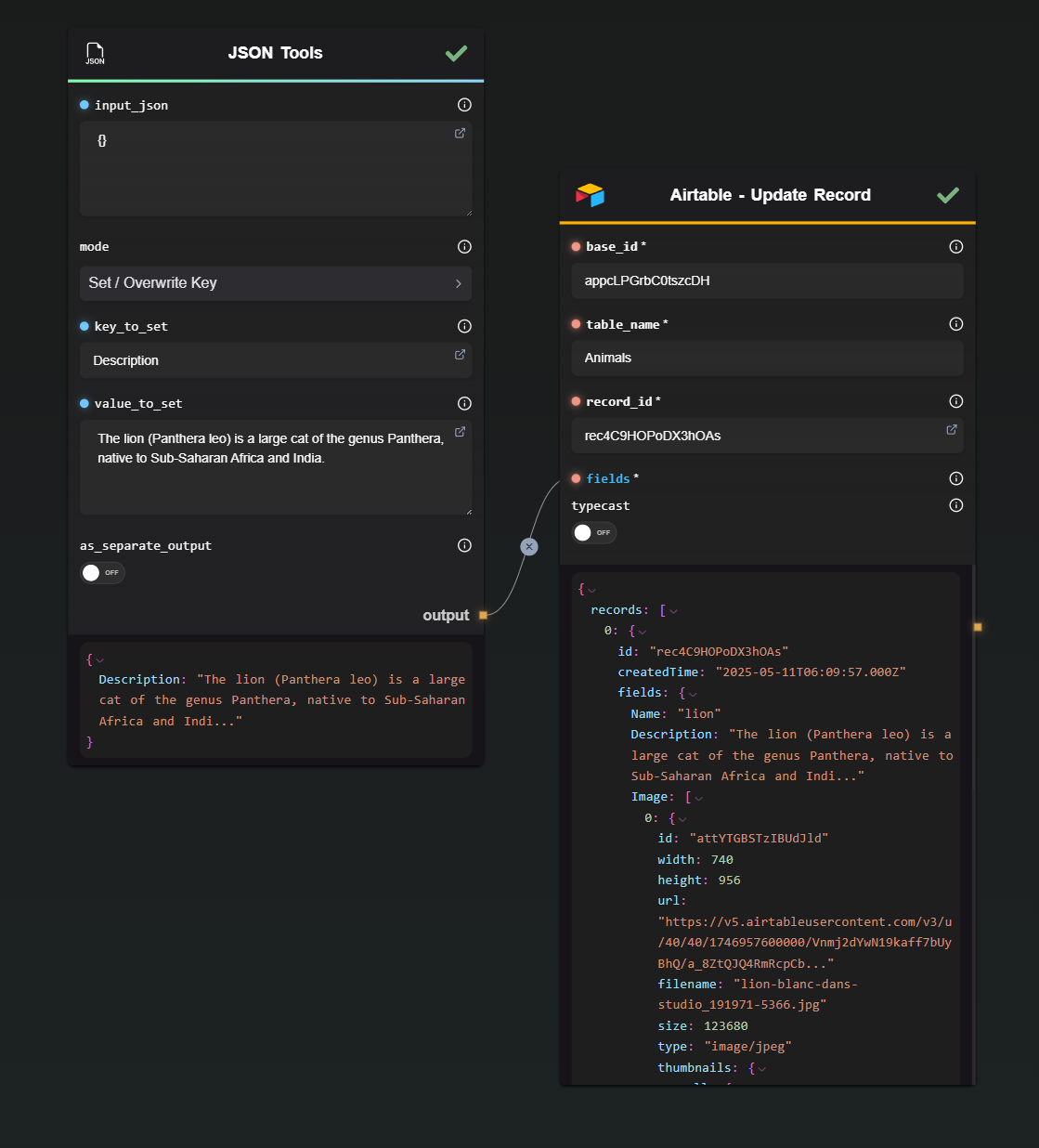
3 · Update Record
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID | The Airtable base to use. |
| Table Name | The table containing the record. |
| Record ID | The record to update. |
| Fields (JSON) | The fields to update. |
| Typecast | Same behavior as in Create. |
4 · Upsert Record
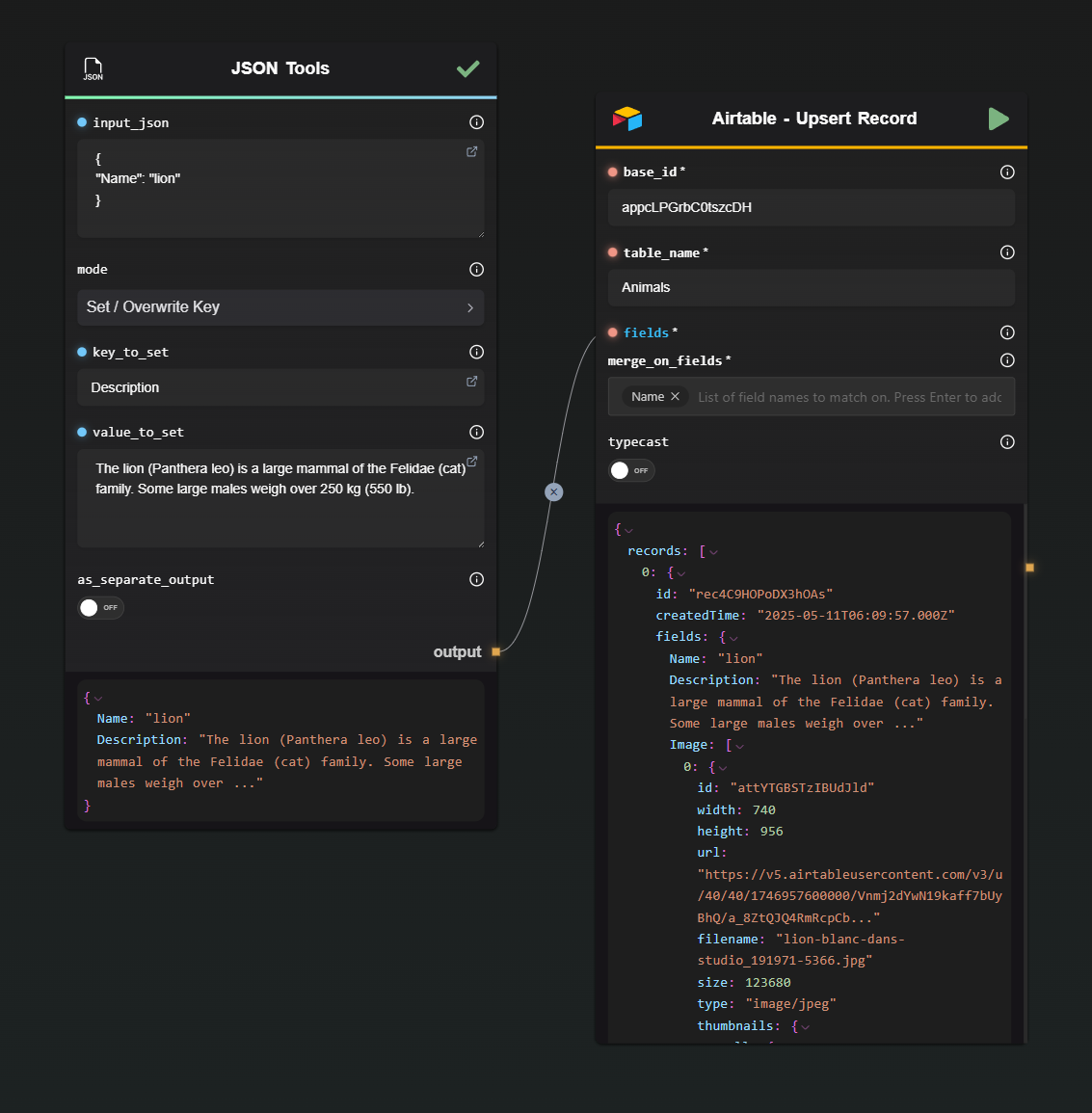
Creates or updates a record in one operation. You don’t need a record ID, but you must specify one or more fields used to determine uniqueness.
In the example below, the 'Name' field is used.
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID / Table Name | The base and table to target. |
| Fields (JSON) | The data to write. |
| Fields To Merge On | One or more column names that uniquely identify the record (e.g., Email). |
| Typecast | Optional coercion. |
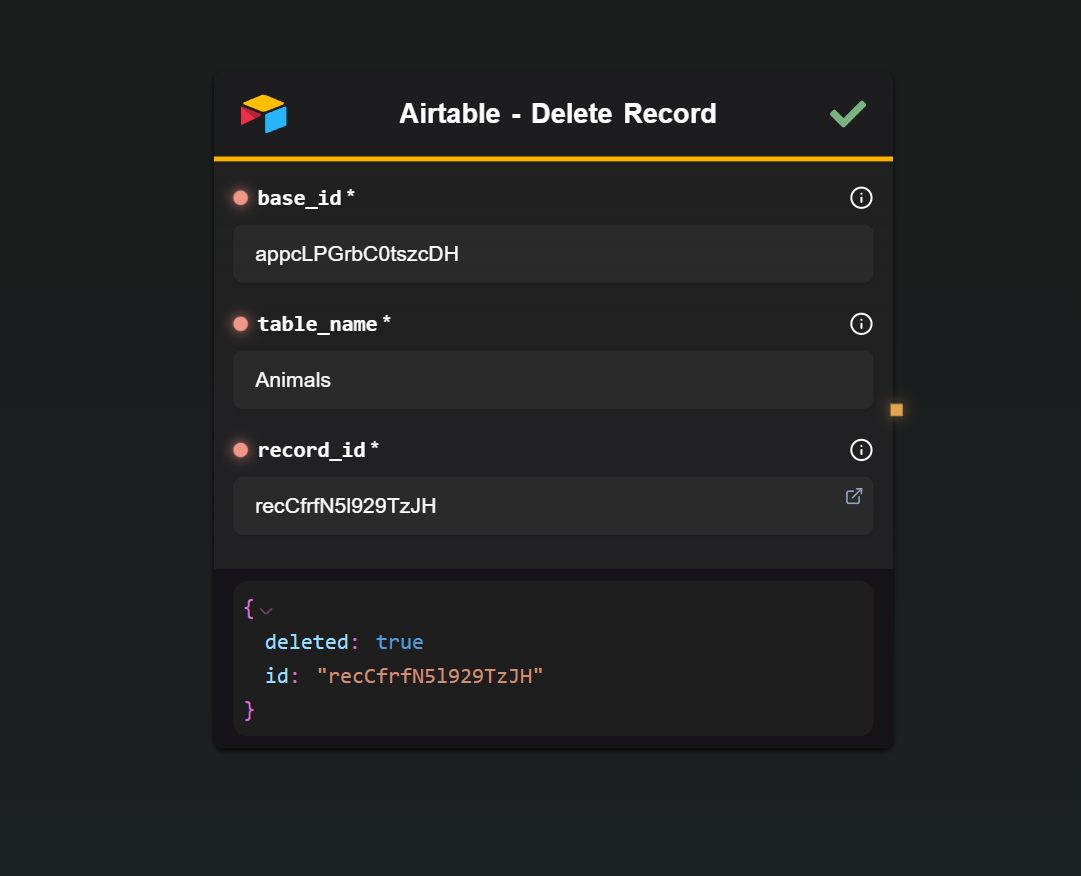
5 · Delete Record
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID / Table Name | The base and table. |
| Record ID | The record to delete. |
Returns Airtable’s deletion payload (or a simple { success: true } if already removed).
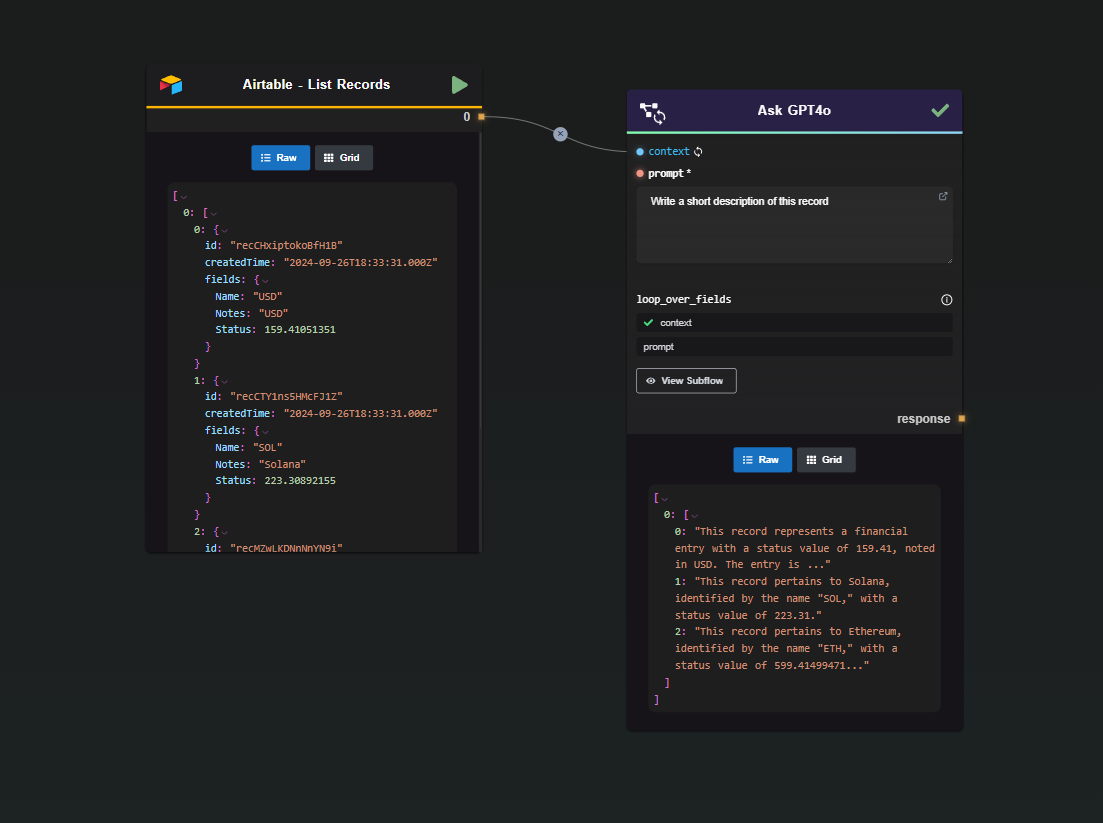
6 · List Records
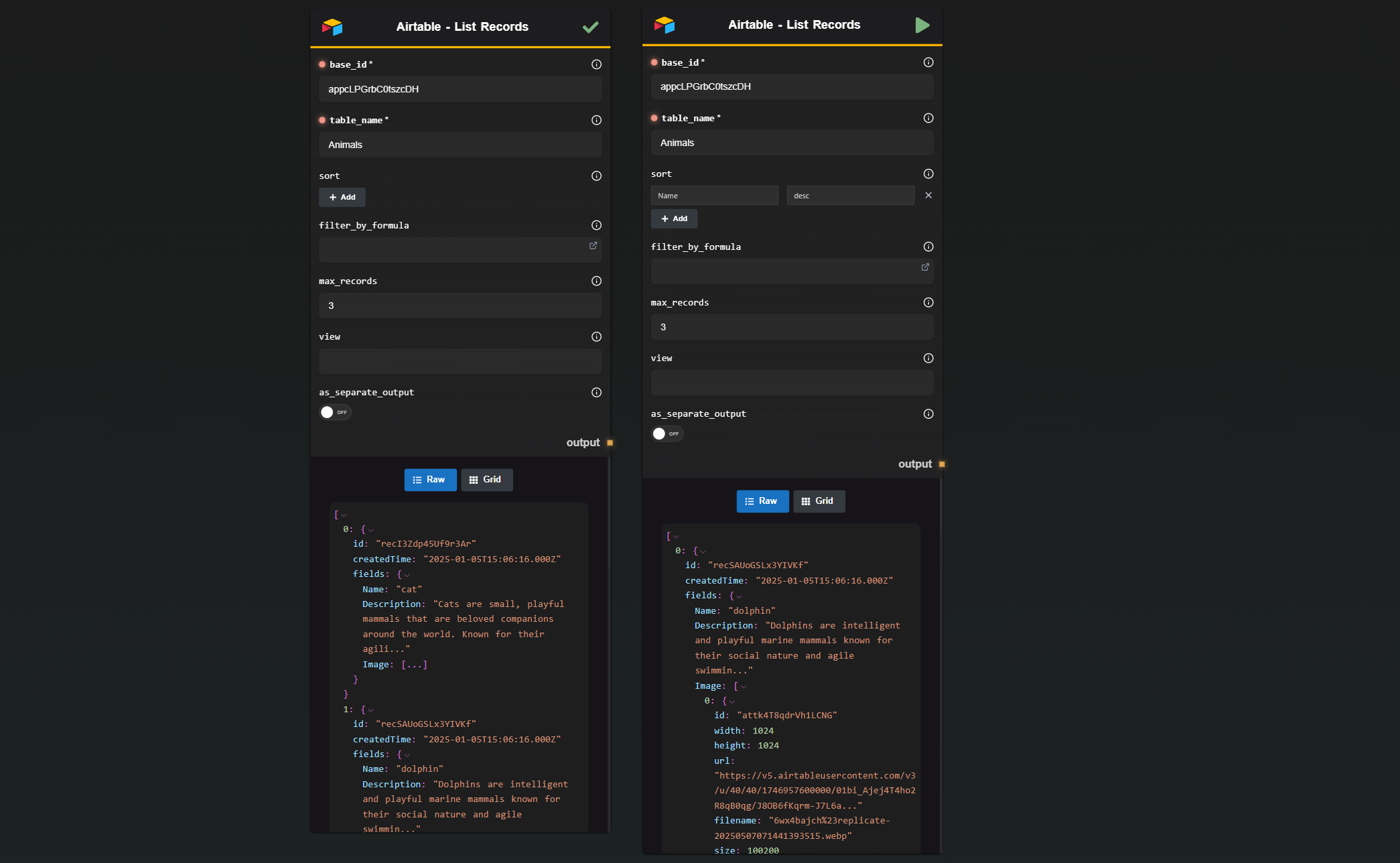
Retrieves rows from any Airtable view in a single call.
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Base ID | The base to query. |
| Table Name | The table to query. |
| Max Records | The maximum number of records to retrieve (default 100, capped at 1000). |
| Sort | Array of { field, direction } objects. Direction is asc or desc. |
| Filter by Formula | An Airtable formula (e.g., {Stage}="Done") applied server-side. |
| View | The name of a view to inherit filters/sorting from. |
| Separate Output | On → each record is output separately. Off → returns one array (useful for loops). |
The node paginates automatically until it hits Max Records or the end of the table, then returns the results as Airtable provides them—no transformations or omissions.
Bulk Variants (Raw JSON)
Need to insert or upsert ten or more records in one call?
Use Create Records or Upsert Records. These take the same parameters as their single-record versions, but expect a JSON array of {"fields": ...} objects.
Field Specifics
Attachments / Multiple Attachments
You can pass:
"FieldName": "https://example.com/photo.jpg"
or:
"FieldName": [
"https://example.com/a.png",
"https://example.com/b.png"
]
The node wraps each URL in the { url: ... } format required by Airtable.
Example (Image field as an attachment):

Single-Select & Multi-Select
Single select → just a string:
"Status": "Done"
Multi-select → either a comma-separated string or an array:
"Tags": "Idea, Doing, Done"
// or
"Tags": ["Idea", "Doing", "Done"]
Collaborator
Provide the collaborator’s email or name, and enable Typecast so Airtable can resolve it to a user ID:
"Assignee": "name@email.com"
Looping Over Results
The List Records node outputs records as an array—ideal for a Subflow Loop. You’ll find several ready-made loop templates in the AI-Flow App.